
Update: A Complete Guide to Subsidy Policies for Culture and Tourism Projects
Source:
Author:
Release time:
2025-02-14
Click to view details
Key Cultural Tourism Event Recommendations
2025 China Tourism, Leisure and Entertainment Industry Annual Conference
March 18-20 · Beijing

Editor | Liu Kaiye
2024 has been a year of vigorous growth for the tourism industry, with cultural tourism consumption becoming a vital force in expanding and boosting consumption. The significant role of "the tourism industry as a new growth point for the national economy and a strategic pillar industry for the national economy" is becoming increasingly prominent. In 2025, with the expansion of the "tourism empowerment effect," governments and cultural tourism departments in various provinces and regions attach great importance to investment and financing in the cultural tourism industry, constantly exploring innovative cultural tourism financing and broadening enterprise financing channels. This article will focus on the policy-backed support funds available for cultural tourism project development.
1. Key Directions: Includes providing basic public cultural service projects, maintenance and equipment procurement for public cultural and sports facilities, talent team building for grassroots public cultural services, and other basic public cultural service projects. The specific expenditure scope of basic public cultural service projects includes reading newspapers, listening to radio, watching TV, watching movies, local opera performances, facility opening services, and cultural and sports activities. Maintenance and equipment procurement for public cultural and sports facilities: (1) Maintenance and equipment procurement for public libraries, cultural centers, museums, memorial halls, theaters, stadiums, radio and television transmission (monitoring) stations, relay stations, satellite earth stations, and broadcasting organizations that retain the nature of public institutions. (2) Maintenance and equipment procurement for art troupes and news publishing units that retain the nature of public institutions; maintenance and protection of cultural relics protection units at or below the provincial level; maintenance and equipment procurement for township and village grassroots comprehensive cultural service centers. (3) Procurement of mobile cultural vehicles.
2. Subsidy Standards: Mobile stage vehicles are assessed at a standard of 500,000 yuan per vehicle; public welfare opera performances (opera going to rural areas) are assessed at a standard of 6 performances per township per year, with a subsidy of 5,000 yuan per performance; public welfare opera performances (free or low-price performances of endangered opera types) are assessed for provincial subsidy funds based on the number of endangered opera types and a calculation standard (100 performances purchased annually at 5,000 yuan per performance), with the specific purchasers, number of performances, and subsidy standards for public welfare performance services determined by the financial departments and cultural and tourism departments of the relevant provinces (autonomous regions, municipalities directly under the central government, cities specifically designated in the state plan, including Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps, hereinafter collectively referred to as provinces), and the implementation plan reported to the Ministry of Culture and Tourism for filing; operating and maintenance fees for central radio and television program wireless coverage are assessed according to current standards; wired high-definition interactive digital set-top boxes in ethnic areas are assessed at a one-time subsidy of 100 yuan per household; and projects to address shortcomings in national fitness venues and equipment are assessed at 200,000 yuan per sub-district (township), with relevant provincial financial departments and sports departments avoiding overlap with projects funded by other central government financial funds when arranging project budgets.
General project subsidy funds adopt the factor allocation method, which includes basic factors, business factors, and financial capacity factors. The allocation amount is calculated based on basic factors and business factors (each accounting for 50% weight), and then adjusted to determine the subsidy amount according to the fiscal difficulty coefficient of each province (autonomous region, municipality) stipulated in the central government's equalization transfer payment method.
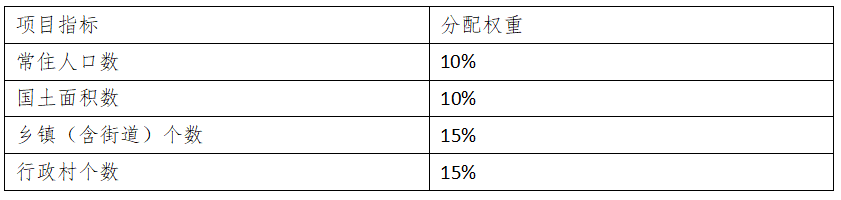
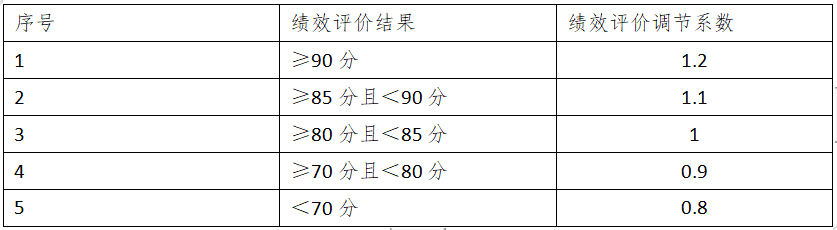
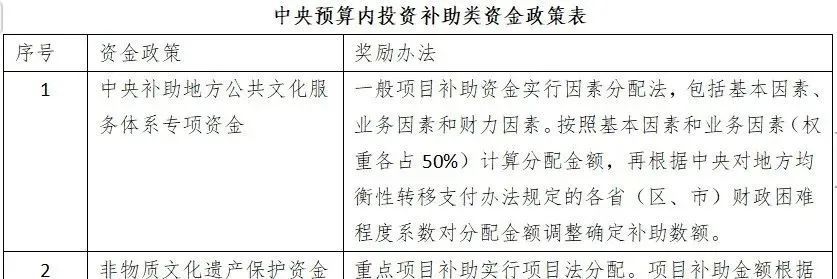

National Cultural Tourism Industry and Project Policies
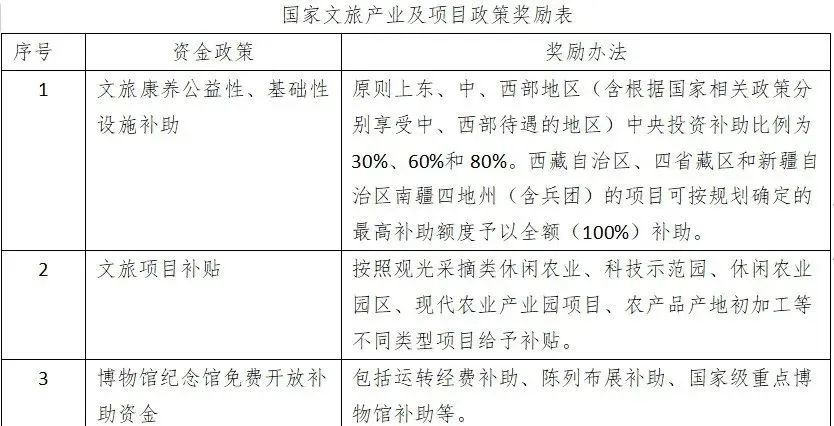
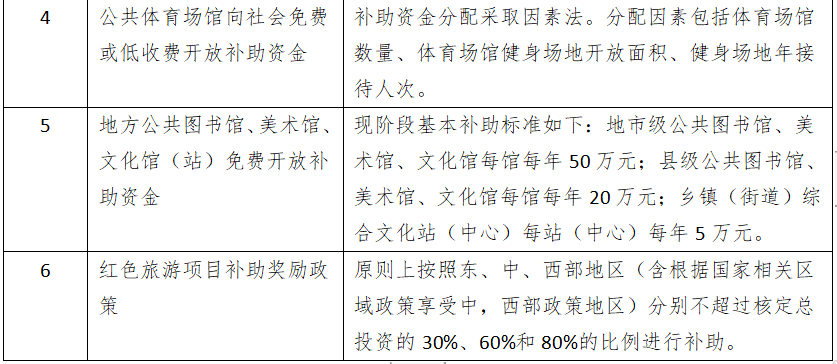
Key Cultural Tourism Event Recommendations
2025 China Tourism, Leisure and Entertainment Industry Annual Conference
March 18-20 Day • Beijing

Key words:












